
Navigating International Packaging Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Takeaways
- Different regions have distinct packaging regulations that must be followed for compliant international shipping
- Food labels require special considerations including ingredient disclosure and allergen warnings
- Material selection impacts regulatory compliance across different markets
- Standardised packaging codes like FEFCO simplify international communication
- Working with specialised packaging manufacturers helps navigate complex regulatory landscapes
- Circular economy principles are increasingly shaping global packaging regulations
- Digital tools are transforming compliance management for international businesses
- Documentation and record-keeping are essential components of regulatory compliance
- Sustainability requirements are becoming mandatory in many jurisdictions
- Anti-counterfeiting measures are increasingly integrated into packaging regulations
Introduction to International Packaging Regulations
International packaging regulations can be challenging to understand for businesses that sell products in different countries. Each country has its own rules about packaging, and you need to follow them all if you want to sell your products there. At Labelprint24, we help businesses make packaging that follows these rules whilst still looking good and protecting what's inside.

The packaging industry has many rules about safety, labels, size standards, and what happens to packaging after it's used. When businesses want to sell in new countries, they need to know these rules. If they don't follow them, they might have to take products back, pay fines, or even face legal problems that can hurt their business and reputation. The complexity of these regulations has increased significantly in recent years, with new requirements emerging around sustainability, traceability, and consumer protection.
Our comprehensive label solutions meet requirements for many international markets, helping businesses follow regulations whilst keeping their brand looking the same everywhere. We think about regulations when we choose materials and printing methods to make sure our packaging works well and follows the rules. Our regulatory compliance team stays updated with the latest changes across different markets to ensure our solutions remain current and effective.
Regional Packaging Regulation Frameworks
European Union Packaging Standards
The European Union has some of the world's most comprehensive packaging rules. They have laws like the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive and the Single-Use Plastics Directive. These rules say what packaging can be made of, how recyclable it needs to be, and set goals for reducing waste. The EU really cares about protecting the environment and making a "circular economy" where materials get reused instead of thrown away.
The EU's approach to packaging regulation is increasingly driven by the European Green Deal, which aims to make Europe climate-neutral by 2050. This has led to more stringent requirements for packaging design, with emphasis on reducing environmental impact throughout the entire lifecycle. The upcoming Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) will introduce even more ambitious targets for recycling, reuse, and waste reduction.

EU packaging rules focus on:
- Material restrictions - Heavy metals and harmful substances with strict limits on cadmium, mercury, lead, and hexavalent chromium (combined concentration must not exceed 100 ppm by weight)
- Minimum recycled content requirements - Becoming increasingly stringent under the European Green Deal, with specific targets for different packaging types (e.g., 30% recycled content for plastic bottles by 2030)
- Clear labelling for consumer information - Including standardised recycling symbols and material identification codes that help consumers make informed decisions about disposal
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) systems - Making manufacturers financially responsible for the end-of-life management of packaging, including collection, sorting, and recycling costs
- Packaging minimisation principles - Encouraging reduction of packaging volume and weight whilst maintaining functionality, with specific requirements for e-commerce packaging
- Essential requirements compliance - Ensuring packaging is manufactured to minimise its impact on the environment and human health whilst maintaining necessary protective functions
- Deposit return systems - Many EU countries are implementing or expanding these systems for beverage containers to increase collection rates
- Single-use plastic restrictions - Bans on certain single-use plastic items and requirements for alternatives or reduction strategies

Our food label solutions follow EU rules, including the Food Information to Consumers Regulation which says what information must be on food packaging. These rules require detailed lists of ingredients, allergy warnings, nutrition facts, and sometimes information about where the food comes from. The regulation also mandates specific font sizes, contrast requirements, and placement guidelines to ensure information accessibility for all consumers, including those with visual impairments.
North American Packaging Regulations
In North America, packaging rules come from many different government agencies. In the United States, the FDA and EPA make rules about packaging. In Canada, Health Canada and Environment and Climate Change Canada do this job. Unlike the EU, which has one set of rules for all countries, North America has different rules at the national, state/province, and sometimes even city levels. This makes it more challenging for manufacturers to keep track of all the rules they need to follow.
The regulatory landscape in North America is characterised by a complex web of federal, state, and local requirements. Recent years have seen increased activity at the state level, with states like California, New York, and Washington leading the way with progressive packaging legislation. This has created a patchwork of requirements that can be particularly challenging for companies operating across multiple states.
Important North American requirements include:
North American Requirements: Food-contact materials regulations establish safety standards for materials that come into contact with food products, including migration testing requirements. Consumer protection laws require warning labels for products containing chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm, which can affect packaging materials containing certain substances like BPA or phthalates. Truth in labelling laws prohibit false or misleading product claims and require accurate representation of contents, including net quantity statements and origin declarations.
Additional Requirements: Recycling and extended producer responsibility programmes include bottle deposit systems and packaging recovery fees in various jurisdictions. Child-resistant packaging requirements apply to certain products including pharmaceuticals and household chemicals. Organic labelling standards have specific requirements for packaging materials used with organic products, including restrictions on synthetic substances. Plastic waste reduction laws in various states target single-use plastics and require minimum recycled content. Municipal packaging ordinances in some cities implement local packaging restrictions and requirements.
Our cardboard box solutions are made to meet North American standards, including size requirements for efficient shipping and handling. We make sure our materials follow FDA rules for food contact when needed, and we can make packaging with the right warning statements to follow regulations. Our North American compliance programme includes regular testing and certification to ensure ongoing conformity with evolving requirements.
Emerging Markets and Regulatory Trends
Emerging markets across Africa, Latin America, and other developing regions are rapidly developing their own packaging regulations, often learning from the experiences of more established regulatory frameworks. These markets present both opportunities and challenges for international businesses, as regulations may be less established but are evolving quickly.
Key trends in emerging markets include:
- Adoption of international standards - Many countries are adopting ISO standards and regional best practices to facilitate international trade
- Focus on local environmental challenges - Regulations often address specific local issues such as marine plastic pollution or waste management capacity
- Gradual implementation timelines - Recognition that industry needs time to adapt, with phased implementation of new requirements
- Emphasis on education and capacity building - Government programmes to help businesses understand and comply with new regulations
- Regional harmonisation efforts - Trade blocs working to align packaging standards across member countries
Industry-Specific Packaging Requirements
Food and Beverage Packaging Regulations
Food and beverage packaging has some of the strictest rules in the world because it directly affects people's health. These rules cover material safety, testing for chemicals that might move from packaging into food, allergy labels, and nutrition information. The rules are meant to keep consumers safe and give them accurate information about what they're buying.
The complexity of food packaging regulations has increased significantly with growing consumer awareness of food safety, allergen management, and nutritional information. Recent developments include enhanced traceability requirements, stricter limits on chemical migration, and expanded allergen labelling requirements to address emerging food sensitivities.
Food packaging must follow specific requirements across multiple areas:
Material Safety and Migration Testing: In the EU, Regulation 1935/2004 says materials that touch food shouldn't transfer harmful components to the food or change how the food tastes or smells. This includes comprehensive testing requirements for chemical migration under various storage conditions and temperature ranges.
FDA Food Contact Regulations: In the US, FDA rules (Title 21) list what additives, polymers, and production aids are allowed in materials that will touch food. These regulations include specific migration limits and testing protocols for different types of packaging materials.
Allergen Labelling Requirements: Clear identification of major allergens on labels is required globally, though specific requirements vary by region. The EU recognises 14 major allergens, whilst the US identifies 9 major allergen groups. Cross-contamination warnings and precautionary labelling are increasingly required.

Nutritional Information Standards: Most developed markets require standardised nutritional labelling, with specific formats, font sizes, and information hierarchies. The EU requires nutritional information per 100g/ml, whilst the US uses serving sizes defined by FDA regulations.
Origin and Traceability Information: Many markets require country of origin labelling and batch/lot identification for traceability purposes. This is particularly important for imported products and organic foods.
Shelf Life and Storage Instructions: Clear indication of use-by or best-before dates, along with storage instructions, is mandatory in most markets. This includes specific requirements for different product categories and temperature-sensitive products.
Our labels for frozen goods are made to work in temperatures as low as -40°C whilst still sticking to the package and remaining readable. This is important for frozen foods that need to stay labelled throughout the cold supply chain. Our labels use special adhesives and materials that don't crack or peel off in freezing conditions, so they keep following the rules throughout the product's life. These labels undergo rigorous testing to ensure performance under thermal cycling conditions typical in frozen food distribution.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Packaging
Pharmaceutical and medical device packaging rules focus on keeping products safe, preventing contamination, and making sure products can be traced. These industries have strict requirements from agencies like the FDA, European Medicines Agency, and national health authorities. The rules are designed to protect patients through careful controls on materials, manufacturing processes, and information that must be included.
The pharmaceutical packaging sector operates under some of the most stringent regulatory requirements globally, with patient safety being the paramount concern. Recent developments include enhanced serialisation requirements to combat counterfeit medicines, stricter child-resistance standards, and improved accessibility features for elderly patients.
Pharmaceutical packaging must meet numerous specific requirements:
Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: The EU Falsified Medicines Directive requires packaging that shows if it has been tampered with and unique identifiers to prevent fake medicines. This includes safety features visible to both patients and healthcare professionals, plus machine-readable codes for verification systems.
Supply Chain Traceability: The US Drug Supply Chain Security Act requires serial numbers on prescription drugs so they can be tracked through the supply chain. This creates a comprehensive system for identifying and tracing prescription medicines from manufacturer to patient.
Sterile Packaging Standards: ISO 11607 sets standards for sterile medical device packaging to keep devices sterile until they're used. This includes specific requirements for barrier materials, seal integrity testing, and validation of sterilisation processes.
Child-Resistant Packaging: Many medications need child-resistant packaging to prevent accidents, with specific testing requirements under standards like ISO 8317. These packages must be difficult for children under 5 to open but accessible for adults, including those with arthritis.
Accessibility Requirements: Packaging must accommodate users with visual impairments or limited dexterity, including Braille labelling in some markets and easy-open features for elderly patients.
Stability and Compatibility Testing: Packaging must be tested to ensure it maintains product stability throughout the shelf life, including compatibility testing between packaging materials and pharmaceutical products.
Regulatory Submission Requirements: Detailed documentation of packaging materials, manufacturing processes, and testing results must be submitted to regulatory authorities as part of product approval processes.
Our booklet labels provide multi-page, space-saving solutions that stick reliably to jars and bottles. They're perfect for pharmaceutical products that need to include lots of information. These clever labels can contain multiple languages, detailed instructions, and comprehensive safety information whilst still looking clean and professional on the product. The labels are designed to meet pharmaceutical industry standards for durability and legibility throughout the product lifecycle.

Cosmetic Product Packaging Regulations
Cosmetic packaging rules vary by region but usually focus on ingredient disclosure, product claims, and safety warnings. The EU Cosmetic Products Regulation, FDA cosmetic labelling requirements, and similar rules in other regions set specific standards for this industry. These rules aim to protect consumers' health and prevent misleading claims whilst still allowing for creative packaging designs that help brands stand out.
The cosmetics industry faces increasingly complex regulatory requirements as consumer awareness of ingredient safety grows and regulators respond with more stringent oversight. Recent trends include enhanced ingredient transparency requirements, stricter substantiation requirements for marketing claims, and expanded safety assessment obligations.
Cosmetic packaging typically needs to include several mandatory elements:
INCI Ingredient Listing: A full list of ingredients using standardised INCI names (International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients), which helps identify ingredients regardless of language. Ingredients must be listed in descending order of concentration, with specific rules for ingredients present at less than 1%.
Country of Origin: Clear indication of where the product was manufactured, with specific formatting requirements varying by market. Some regions also require identification of the responsible person or company within their jurisdiction.
Usage Instructions and Warnings: Detailed instructions for use and safety warnings, especially for products with certain ingredients or special applications. This includes specific warnings for products intended for use near the eyes or on sensitive skin areas.
Period After Opening (PAO): Indication of how long the product stays good after opening, typically shown with a jar symbol containing a number followed by 'M' for months. This helps consumers understand product lifespan once opened.

Responsible Person Information: In the EU, identification of a responsible person or company who ensures the product follows regulations, including contact information for consumer enquiries and regulatory compliance.
Batch Identification: Clear batch or lot codes for traceability purposes, essential for quality control and product recall procedures if necessary.
Claims Substantiation: Any marketing claims made on packaging must be supported by appropriate evidence, with increasing scrutiny from regulatory authorities on environmental and performance claims.
Our cosmetic labels are made to stay stuck even when they get wet or come in contact with creams and oils. This ensures they follow regulations throughout the product's life. These specialised labels use materials and adhesives that don't break down when exposed to product ingredients, and they keep their print quality and readability even in bathroom environments. Our cosmetic label solutions undergo extensive testing for chemical resistance and durability.
Electronics and Technical Product Packaging
Electronics packaging faces unique challenges including static electricity protection, electromagnetic compatibility, recycling requirements for electronic components, and compliance with various international standards such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment).
Key requirements for electronics packaging include:
- Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection - Specialised materials and designs to prevent static electricity damage during handling and shipping
- EMC compliance - Packaging that doesn't interfere with electromagnetic compatibility testing and certification
- RoHS compliance - Ensuring packaging materials don't contain restricted hazardous substances like lead, mercury, or certain flame retardants
- WEEE compliance - Packaging must support proper identification and separation of electronic components for recycling
- Conflict minerals disclosure - Some regions require information about conflict minerals in electronic products and their packaging
- Energy labelling - Many electronics require energy efficiency labels with standardised formats and testing protocols
Material Compliance and Safety Standards
Food-Contact Material Regulations
Materials that touch food directly must meet strict safety requirements to prevent harmful substances from getting into the food. These rules vary by region but generally require testing to make sure materials don't transfer components to food in amounts that could be dangerous to health. The rules cover not just the base materials but also additives, coatings, adhesives, and printing inks used in food packaging.
The regulatory landscape for food-contact materials has become increasingly sophisticated, with advancing analytical methods enabling detection of smaller quantities of migrating substances and new research revealing potential health impacts of previously unconsidered chemicals. This has led to more comprehensive testing requirements and stricter migration limits.
Food-contact material regulations encompass several key areas:
EU Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004: Sets general principles for all food contact materials, establishing that materials should not transfer their constituents to food in quantities that could endanger human health or bring about an unacceptable change in the composition of the food or a deterioration in its organoleptic characteristics.
EU Plastic Materials Regulation (EU) No 10/2011: Sets specific limits for substances used in plastic food contact materials and specifies how to test for compliance. This regulation includes a positive list of authorised substances and specific migration limits for each substance.
US FDA Regulations (21 CFR 175-178): Cover indirect food additives, including adhesives, coatings, paper, and polymeric materials used in food packaging. These regulations establish what substances may be used and under what conditions.
China's GB 9685 Standard: Lists substances permitted in food packaging and establishes specific migration limits. China has been harmonising its standards with international best practices whilst addressing specific local concerns.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Require food contact materials to be produced under controlled conditions to ensure consistent safety and quality. This includes requirements for facility design, personnel training, and quality control systems.
Testing and Certification Requirements: Comprehensive testing protocols for chemical migration under various conditions simulating real-world use, including different temperatures, contact times, and food simulants.
Our stand-up pouches for drinks are made using food-safe materials that follow international standards. They provide odourless and tasteless packaging that keeps product quality intact. These pouches are thoroughly tested to make sure they meet migration limits and maintain product integrity throughout the shelf life. Our food-contact materials undergo regular third-party testing to verify continued compliance with evolving standards.

Restricted Substances and Chemical Regulations
Various regulations limit the use of certain chemicals in packaging materials to protect people's health and the environment. These include heavy metals, phthalates, BPA, and other concerning substances. Following these regulations requires careful selection of materials, management of suppliers, and sometimes testing to verify that restricted substances are absent or present only at acceptable levels.
The scope of chemical restrictions in packaging continues to expand as scientific understanding of health and environmental impacts improves. Regulatory authorities are increasingly adopting precautionary approaches, restricting substances where potential risks are identified even before conclusive evidence of harm is established.
Major chemical regulations affecting packaging are found across many jurisdictions and include comprehensive frameworks for chemical safety in packaging materials.
Chemical Registration Requirements: Comprehensive regulations for chemical substances require registration of chemicals used in packaging and restrict substances of very high concern. This includes requirements for safety data sheets and communication throughout the supply chain.
Heavy Metal Restrictions: International packaging directives limit heavy metals, restricting the combined concentration of lead, cadmium, mercury, and hexavalent chromium to very low levels by weight. Similar restrictions exist in many markets worldwide.
Consumer Protection Requirements: Various jurisdictions require warning labels for products containing chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm, which can include certain packaging components such as printing inks or adhesives containing restricted substances.
BPA and Related Restrictions: Many countries have banned BPA (bisphenol A) in food contact materials, especially for products intended for babies and young children. These restrictions are expanding to include other bisphenols like BPS and BPF.
Phthalate Restrictions: Many jurisdictions restrict the use of certain phthalates in packaging, particularly for products intended for children or food contact applications.
Environmental Pollutant Controls: International regulations restrict certain long-lasting environmental contaminants that can be present in some packaging materials, with ongoing additions to the restricted lists.
Emerging Chemical Restrictions: Growing restrictions on PFAS substances in food packaging due to environmental persistence and potential health concerns.
Our folding boxes with tuck-in flap are made using materials that follow international chemical safety standards, making them suitable for many applications including food products. We maintain detailed documentation on material composition and regularly test our products to verify they follow chemical restrictions. Our supplier qualification programme ensures all materials meet our stringent chemical compliance requirements.
Transportation and Shipping Safety Standards
Packaging for international shipping must meet various standards to ensure products are protected during transit and handling. These include material strength requirements, stacking tests, and special provisions for hazardous materials packaging. Following these standards is essential for preventing damage, ensuring worker safety, and meeting carrier and customs requirements.
International shipping presents unique challenges for packaging, with products potentially experiencing extreme temperature variations, humidity changes, rough handling, and long transit times. Regulatory requirements have evolved to address these challenges whilst also considering environmental impact and cost efficiency.
Key transportation packaging standards include:
ISO 3394 for Package Dimensions: Establishes preferred sizes for transport packages to optimise logistics efficiency and compatibility with handling equipment. This modular system is based on standard pallet dimensions and helps maximise container utilisation.
ISTA Testing Procedures: The International Safe Transit Association provides testing protocols that evaluate how packaging will withstand various distribution hazards including drops, vibration, compression, and environmental conditions. Different test series address various shipping methods and product fragility levels.
UN Recommendations for Dangerous Goods: Specify detailed requirements for packaging materials, construction, and testing for products classified as hazardous. This includes specific UN packaging codes and certification requirements for different hazard classes.
ISPM-15 for Wood Packaging: The International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures requires heat treatment or fumigation of wooden packaging materials in international trade to prevent the spread of pests and diseases. This affects pallets, crates, and other wood packaging components.
Carrier-Specific Requirements: Major shipping companies often have their own requirements for weight limits, dimensional restrictions, and packaging strength specifications that may be more stringent than regulatory minimums.
Temperature Control Standards: For temperature-sensitive products, specific standards govern insulated packaging, refrigerated containers, and temperature monitoring systems.
Our custom corrugated board sheets help prevent packaged goods from slipping during transport and can be used as cushioning material for extra protection. These versatile packaging components can be produced in various flute profiles and material weights to meet specific transportation requirements for different products and shipping conditions. Our transportation packaging undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets international shipping standards.

Labelling and Information Disclosure Requirements
Mandatory Label Elements by Region
Different regions require specific information to be shown on product labels. These requirements typically include product identification, quantity declarations, manufacturer information, and various mandatory warnings or symbols. Following these diverse requirements often means creating region-specific label designs or finding clever solutions that can include varying information requirements.
The complexity of labelling requirements has increased significantly in recent years, driven by consumer protection legislation, environmental concerns, and the need for enhanced traceability. Modern labelling must balance regulatory compliance with aesthetic appeal and functional requirements such as durability and readability.
Common mandatory label elements vary significantly by region:
European Union Requirements: The EU has comprehensive labelling requirements that include conformity marking for products meeting safety standards, demonstrating compliance with applicable directives. Producer responsibility symbols indicate participation in packaging recovery systems. Recyclability symbols identify recyclable materials with specific coding for different material types. Food labelling follows comprehensive regulations requiring nutritional information, allergen declarations, and origin information.
North American Requirements: Standardised nutrition panels are required for food products with specific formatting and content requirements. Organic certification marks are required for qualifying products. Various federal and state warning statements may be required for products containing certain chemicals. Net quantity statements must follow specific formatting rules under consumer protection legislation.

Asian Market Requirements: Many countries require specific recycling symbols according to material type, using standardised icons to help consumers properly sort packaging waste. Industrial standards markings are required for certain product categories. Food products require detailed labelling in local languages including ingredient lists and nutritional information.
Global Requirements: Hazard symbols are used worldwide for dangerous substances, providing standardised pictograms to communicate specific hazards regardless of language barriers. These symbols must meet specific size, colour, and placement requirements. Most markets require country of origin declarations, though the exact specifications for presentation vary. Some countries require "Made in [Country]" statements, whilst others accept manufacturing location information.
Our self-adhesive paper labels stick well to almost all surfaces and can be customised to include all required regulatory information with perfect print quality. We offer various paper types, adhesives, and finishing options to ensure labels meet specific market requirements whilst maintaining brand aesthetics. Our design team has extensive experience in regulatory compliance across different markets.
Language Requirements and Multilingual Packaging
Many countries require product information to be presented in their official language(s), which creates challenges for international marketers. Some regions, like the EU, have specific requirements for multilingual packaging to serve their diverse populations. Addressing these requirements efficiently whilst maintaining packaging aesthetics and brand consistency requires strategic approaches to label design and information presentation.
The challenge of multilingual packaging extends beyond simple translation to include cultural considerations, reading patterns, regulatory compliance in multiple languages, and space optimisation. Modern packaging must accommodate diverse linguistic requirements whilst maintaining visual appeal and functional effectiveness.
Multilingual packaging considerations include:
Regional Flexibility: Many regions require information in local languages of each market, but allow flexibility in implementation. Essential product information must be provided in the official language(s) of each jurisdiction where the product is sold. Some information can be provided through multilingual labels or accompanying documentation.
Bilingual Requirements: Some markets require bilingual labelling under consumer protection legislation, with mandatory information in multiple official languages. Specific formatting rules govern the presentation of multilingual information, including font size relationships and placement requirements.
Multilingual Standards: Certain regions require multiple languages on products sold throughout their territory, reflecting multilingual populations. Some products may use additional languages as well, depending on the target market and product category.
Space Management Challenges: Including multiple languages often requires innovative label designs or supplementary information solutions. This includes fold-out labels, booklet labels, QR codes linking to translated information, or region-specific packaging variations.
Legibility Requirements: Font size requirements ensure information remains legible even when multiple languages must fit in limited space. Regulatory authorities specify minimum character heights and contrast requirements for different types of information.
Translation Quality Standards: Accurate translation is crucial for regulatory compliance and consumer safety. This includes proper terminology for technical terms, allergens, and safety warnings. Some markets require certified translations for certain product categories.
Our booklet labels for cosmetic products offer a smart solution for multilingual requirements, providing multiple pages in a compact format that sticks reliably to packaging. These innovative labels can contain extensive information in numerous languages whilst maintaining a clean, uncluttered appearance on the product. The booklet format allows for detailed regulatory information without compromising package aesthetics.

Traceability and Product Identification Standards
Modern supply chains need effective traceability systems to track products from manufacture to consumption. Various standards and regulations require specific identification systems for different product categories. These systems support product authentication, recall management, inventory control, and consumer information access through standardised coding and identification technologies.
Traceability has become increasingly important due to globalised supply chains, enhanced consumer expectations for transparency, and regulatory requirements for rapid response to safety issues. Digital technologies are transforming traceability capabilities, enabling real-time tracking and consumer engagement.
Key traceability standards encompass multiple technologies and applications:
GS1 Standards: Provide globally recognised systems for product identification through various coding technologies. This includes UPC and EAN barcodes for basic product identification, DataMatrix codes for space-constrained applications, and QR codes for consumer engagement. GS1 standards ensure global interoperability and supply chain efficiency.
Food Traceability Requirements: The EU Food Information to Consumers Regulation requires batch or lot codes to help trace products if safety issues arise. These codes must enable identification of production dates, processing facilities, and ingredient sources. Enhanced traceability is required for certain high-risk food categories.
Pharmaceutical Serialisation: EU FMD (Falsified Medicines Directive) and US DSCSA (Drug Supply Chain Security Act) mandate unique identifiers for prescription medications. These systems enable verification of authenticity and tracking throughout the supply chain, helping combat counterfeit medicines.
ISO 22005 Food Traceability: Establishes principles and requirements for designing and implementing traceability systems throughout the food supply chain. This standard provides guidance on documentation, record-keeping, and system verification.
Digital Enhancement Technologies: QR codes enable consumers to access additional product information, verification systems, or interactive content through smartphone scanning. NFC (Near Field Communication) technology provides similar capabilities with enhanced security features.

Blockchain Integration: Emerging technologies provide immutable records of product journey from source to consumer, enhancing transparency and enabling rapid response to quality or safety issues.
Our unprinted paper labels are perfect for in-house printing of variable data like batch codes, expiration dates, and serialisation information required for regulatory compliance. These labels provide a versatile foundation for implementing traceability systems that can be customised to specific product and market requirements. Our labels are compatible with various printing technologies including thermal transfer, laser, and inkjet systems.
Dimensional Standards and Structural Requirements
International Standardisation of Packaging Dimensions
Standardised packaging dimensions help with efficient logistics, storage, and handling throughout the supply chain. Various international standards establish preferred dimensions for different packaging types. Following these standards can reduce transportation costs, improve warehouse space utilisation, and enhance compatibility with automated handling systems whilst ensuring products arrive safely at their destination.
The trend towards standardisation reflects the globalisation of supply chains and the need for interoperability across different transportation modes, handling equipment, and storage systems. Modern logistics operations rely heavily on dimensional consistency to achieve efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Important dimensional standards include several key frameworks:
ISO 3394 Transport Packaging: Establishes a modular system based on the 600mm x 400mm footprint with standardised height increments to optimise logistics efficiency. This system ensures maximum compatibility with handling equipment, storage systems, and transportation vehicles. The modular approach allows for efficient nesting and stacking of packages.
ISO 780 Handling Instructions: Provides standardised graphical symbols for package handling to communicate proper handling requirements regardless of language. These symbols cover requirements such as "this way up," "fragile," "keep dry," and temperature limitations, ensuring consistent handling throughout the supply chain.
FEFCO Structural Standards: Standardise corrugated box designs through internationally recognised numerical codes that specify exact construction methods. This system enables precise communication of packaging requirements across different countries and suppliers.
Pallet Compatibility: Modular dimensions based on international pallet standards ensure packaging efficiently utilises pallet space to maximise shipping density and minimise waste. Standard pallet sizes vary by region but follow established dimensional principles.
Container Optimisation: Packaging dimensions that optimise use of standard shipping containers help reduce transportation costs and environmental impact through improved load efficiency.
UN Dangerous Goods Standards: Specify exact dimensional requirements for packages containing hazardous materials to ensure safe transport and compatibility with specialised handling equipment.
Our cardboard sheets cut to size can be produced according to international dimensional standards, ensuring compatibility with global logistics systems. We can manufacture these sheets in precise dimensions to fit specific packaging applications whilst meeting international standards for material quality and performance. Our production capabilities include custom sizing for unique applications whilst maintaining structural integrity.
FEFCO Standards for Corrugated Packaging
The International Fibreboard Case Code, created by FEFCO (European Federation of Corrugated Board Manufacturers), provides standardised designs for corrugated boxes that are recognised worldwide. These codes make communication easier between packaging designers, manufacturers, and users. By referring to a specific FEFCO code, businesses can precisely specify box constructions without lengthy descriptions or technical drawings, making communication clear across language barriers and technical specialties.
FEFCO codes have become the international language of corrugated packaging, enabling efficient communication across global supply chains. The system continues to evolve with new codes added to address emerging packaging needs and innovative structural designs.
Common FEFCO codes include several widely-used designs:
FEFCO 0201 - Regular Slotted Container: The most common box style with flaps of equal length that meet at the centre when closed. This design provides a versatile and economical packaging solution suitable for a wide range of products. The RSC design offers good stacking strength and is compatible with most automated packaging equipment.
FEFCO 0211 - Folding Box with Tuck-in Flap: Offers a secure closure without requiring tape or glue, making it ideal for retail products and easy consumer access. This design provides excellent presentation value whilst maintaining structural integrity. The tuck-in mechanism allows for easy opening and reclosing.
FEFCO 0110 - Corrugated Sheet/Pad: Provides protective cushioning and separation between products or reinforcement for other packaging components. These sheets can be customised with perforations, creasing, or special coatings for specific applications.
FEFCO 0228 - Folding Box with Separator: Features an integrated divider that creates compartments for organising or protecting multiple items within a single package. This design eliminates the need for separate partition materials and simplifies packing operations.
FEFCO 0427 - Telescopic Design: Separate lid and bottom components offer enhanced stacking strength and premium presentation for higher-value products. This design provides excellent protection and an upscale appearance suitable for gift packaging or luxury products.
FEFCO 0713 - Wraparound Case: Efficient design that wraps around products with minimal material usage whilst providing excellent graphics display area for branding and product information.
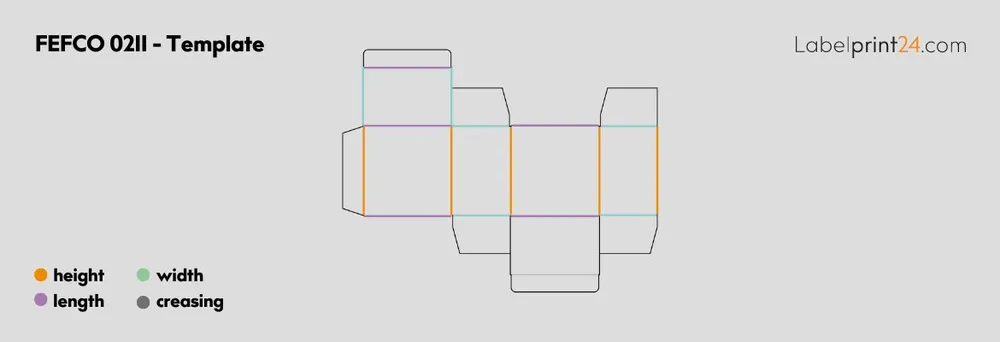
We offer various FEFCO standard packaging solutions, including FEFCO 0211 folding boxes and FEFCO 0110 corrugated sheets, ensuring international compatibility and recognition. These standardised designs can be customised with printing, special coatings, or size adjustments whilst maintaining their fundamental structural integrity and performance characteristics. Our design team can recommend the most appropriate FEFCO code for specific product requirements.
Specialised Packaging Structures for Specific Products
Certain products need specialised packaging structures to ensure protection, compliance with regulations, and consumer usability. These structures often have specific standards and testing requirements. From fragile items needing extra cushioning to hazardous materials requiring containment features, specialised packaging addresses unique product characteristics and handling challenges whilst meeting regulatory requirements.
The development of specialised packaging structures reflects the increasing sophistication of products and regulatory requirements. Modern packaging engineering combines material science, structural design, and regulatory compliance to create solutions that protect products whilst enhancing user experience.
Specialised packaging structures address various specific needs:
Child-Resistant Packaging: Governed by ISO 8317 and 16 CFR 1700 for pharmaceuticals and hazardous household products, these packages incorporate mechanisms that are difficult for young children to open but accessible for adults, including seniors. Testing protocols ensure effectiveness whilst maintaining accessibility for intended users.
Tamper-Evident Designs: Provide visible evidence if a package has been opened or compromised, enhancing product security and consumer confidence. These features are particularly important for pharmaceuticals, food products, and consumer goods where product integrity is crucial.
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): Alters the gas composition within the package to extend shelf life by slowing oxidation and microbial growth processes. This technology requires specialised barrier materials and precise gas mixing capabilities.
Shock-Absorbing Structures: Incorporate cushioning elements, suspension designs, or specialised materials to protect contents from impact damage during handling and shipping. These designs often require extensive testing to validate protection effectiveness.
Temperature-Controlled Packaging: Maintains specific temperature ranges through insulation materials and phase-change components for pharmaceuticals and certain food products. These systems require careful design to maintain temperature integrity throughout the supply chain.
Anti-Static Packaging: Protects electronic components from electrostatic discharge damage using specialised materials and design features that safely dissipate static electricity.
Barrier Packaging: Provides protection against moisture, oxygen, light, or other environmental factors that could degrade product quality. Multi-layer structures combine different materials to achieve specific barrier properties.
Our folding box with separator features an integrated bar that separates the interior into two halves, preventing items from touching during transport—ideal for fragile products or sets. This specialised structure provides organisation and protection without requiring additional packaging components, making assembly simpler and reducing material usage. The separator design can be customised for different product configurations and protection requirements.

Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Circular Economy Regulations
The circular economy concept is driving new packaging regulations worldwide, focusing on designing out waste, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. This approach requires rethinking traditional packaging design to prioritise reusability, recyclability, and reduced environmental impact throughout the entire lifecycle.
Key circular economy initiatives include:
- Design for circularity requirements - Regulations mandating packaging design that facilitates reuse, recycling, or composting
- Material restriction frameworks - Limitations on materials that cannot be effectively recycled or cause environmental harm
- Recycled content mandates - Minimum percentages of recycled materials required in packaging across various categories
- Reuse and refill systems - Requirements or incentives for packaging systems that can be reused multiple times
- Digital product passports - Emerging requirements for digital tracking of materials and recycling information
Carbon Footprint and Life Cycle Assessment Requirements
Growing regulatory requirements for carbon footprint disclosure and life cycle assessment (LCA) are pushing companies to evaluate and report the environmental impact of their packaging throughout its entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
Environmental assessment requirements encompass:
- Carbon footprint calculations - Standardised methodologies for measuring and reporting packaging-related emissions
- LCA documentation - Comprehensive assessment of environmental impacts across all lifecycle stages
- Supply chain transparency - Requirements for disclosure of materials sourcing and manufacturing processes
- Renewable energy usage - Reporting requirements for energy sources used in packaging production
- Water usage and waste generation - Disclosure of resource consumption in packaging manufacturing
Digital Compliance and Future Trends
Digital Labelling and QR Code Integration
Digital technologies are transforming packaging compliance, with QR codes and other digital tools enabling enhanced information sharing, real-time updates, and improved traceability. These technologies allow packaging to carry much more information than traditional labels whilst maintaining clean aesthetic appeal.
Digital compliance trends include:
- Smart labelling systems - QR codes linking to comprehensive product information, ingredient details, and sustainability data
- Real-time regulatory updates - Digital systems allowing compliance information to be updated without package redesign
- Consumer engagement platforms - Interactive features enabling direct communication between brands and consumers
- Blockchain verification - Immutable records of product authenticity and supply chain compliance
- Augmented reality features - Enhanced product information and compliance verification through mobile applications
Artificial Intelligence in Compliance Management
AI technologies are increasingly being used to manage complex compliance requirements, predict regulatory changes, and optimise packaging design for multiple market requirements simultaneously. This technology helps companies navigate the growing complexity of international packaging regulations.
AI applications in packaging compliance include:
- Regulatory monitoring systems - Automated tracking of regulatory changes across multiple jurisdictions
- Compliance verification tools - AI-powered systems that verify label compliance across different markets
- Predictive compliance modelling - Analysis of regulatory trends to anticipate future requirements
- Design optimisation algorithms - AI systems that optimise packaging design for multiple regulatory requirements simultaneously
- Risk assessment tools - Automated evaluation of compliance risks across different markets and product categories
Best Practices for International Compliance
Developing a Global Compliance Strategy
Type your textSuccessful navigation of international packaging regulations requires a systematic approach that balances compliance requirements with business objectives. Companies must develop comprehensive strategies that account for regulatory variations whilst maintaining operational efficiency and brand consistency.
Essential elements of a global compliance strategy include:
- Regulatory mapping and monitoring - Systematic identification and tracking of applicable regulations across all target markets
- Risk-based prioritisation - Focus resources on markets and product categories with highest compliance risks and business impact
- Cross-functional collaboration - Integration of legal, regulatory, marketing, and supply chain teams in compliance planning
- Supplier qualification programmes - Ensuring all packaging suppliers meet relevant regulatory and quality standards
- Documentation and record-keeping systems - Comprehensive systems for maintaining compliance evidence and audit trails
- Training and awareness programmes - Regular education for staff involved in packaging decisions and supply chain management
- Technology integration - Use of digital tools and platforms to streamline compliance management and monitoring
Working with Regulatory Consultants and Testing Laboratories
The complexity of international packaging regulations often requires external expertise to ensure compliance and avoid costly mistakes. Building relationships with qualified consultants and accredited testing laboratories is essential for many companies.
Key considerations when selecting external partners include:
- Accreditation and credentials - Verification of consultant qualifications and laboratory accreditations relevant to your markets
- Market expertise - Specific knowledge of regulations in your target markets and industry sectors
- Testing capabilities - Comprehensive testing services covering all relevant safety, performance, and regulatory requirements
- Regulatory monitoring services - Ongoing surveillance of regulatory changes and their impact on your products
- Global coverage - Ability to support compliance across multiple markets through direct presence or partner networks
- Integration capabilities - Ability to work seamlessly with your internal teams and existing processes
Supply Chain Management for Compliance
Effective compliance requires careful management of the entire packaging supply chain, from raw material suppliers to final packaging converters. Each link in the chain must understand and meet relevant regulatory requirements.
Supply chain compliance best practices include:
- Supplier auditing programmes - Regular assessment of supplier compliance capabilities and performance
- Material traceability systems - Complete documentation of material sources and processing history
- Quality agreements - Formal contracts specifying compliance requirements and responsibilities
- Change control procedures - Systematic management of any changes to materials, processes, or suppliers
- Contingency planning - Alternative suppliers and materials to ensure continuity in case of compliance issues
- Performance monitoring - Regular review of supplier compliance performance and corrective action when needed
Common Compliance Challenges and Solutions
Managing Regulatory Conflicts Between Markets
One of the most challenging aspects of international packaging compliance is managing situations where different markets have conflicting requirements. These conflicts can arise from different safety philosophies, environmental priorities, or technical standards.
Strategies for managing regulatory conflicts include:
- Highest common denominator approach - Meeting the most stringent requirements across all markets
- Market-specific packaging variants - Developing different packaging solutions for markets with incompatible requirements
- Modular design systems - Creating packaging platforms that can be adapted for different regulatory requirements
- Regulatory advocacy - Working with industry associations to promote harmonisation of conflicting standards
- Risk-based decision making - Prioritising compliance efforts based on market importance and enforcement likelihood
Keeping Up with Rapid Regulatory Changes
Packaging regulations are evolving rapidly, particularly in areas related to sustainability, food safety, and consumer protection. Companies must develop systems to stay current with these changes and adapt their packaging accordingly.
Effective regulatory monitoring systems include:
- Multi-source information gathering - Monitoring government publications, industry associations, and expert networks
- Impact assessment procedures - Systematic evaluation of how regulatory changes affect existing products and packaging
- Timeline management - Planning for compliance implementation considering development and approval timelines
- Stakeholder communication - Clear communication of regulatory changes and their implications throughout the organisation
- Continuous improvement processes - Regular review and enhancement of monitoring and response capabilities
Cost Management in Compliance
Compliance with international packaging regulations can be expensive, particularly for companies operating in many markets. Effective cost management requires strategic approaches that balance compliance requirements with business economics.
Cost management strategies include:
- Standardisation where possible - Using common packaging solutions across multiple markets to achieve economies of scale
- Phased implementation - Prioritising high-volume or high-risk markets for initial compliance efforts
- Technology leverage - Using digital tools and automation to reduce ongoing compliance management costs
- Supplier partnerships - Collaborating with packaging suppliers who can provide compliant solutions across multiple markets
- Risk-based resource allocation - Focusing compliance investments on areas with highest business impact
Future Outlook for Packaging Regulations
Anticipated Regulatory Trends
The regulatory landscape for packaging continues to evolve rapidly, driven by environmental concerns, technological advances, and changing consumer expectations. Understanding likely future trends helps companies prepare for upcoming requirements.
Key trends shaping future regulations include:
- Enhanced sustainability requirements - Stricter recycled content mandates, design for circularity rules, and carbon footprint disclosure requirements
- Digital integration mandates - Requirements for digital product information, traceability systems, and smart packaging features
- Microplastics regulations - New restrictions on packaging materials and designs that contribute to microplastic pollution
- Enhanced food safety standards - Stricter migration limits, expanded testing requirements, and new safety assessment protocols
- Consumer accessibility requirements - Mandatory features for elderly and disabled consumers, including easy-open designs and clear labelling
- Global harmonisation efforts - Increased coordination between regulatory authorities to reduce conflicts and complexity
Preparing for Regulatory Evolution
Companies that successfully navigate future regulatory changes will be those that build adaptability into their packaging strategies and compliance systems. This requires forward-thinking approaches and flexible implementation capabilities.
Preparation strategies include:
- Scenario planning - Developing contingency plans for different regulatory evolution scenarios
- Technology investment - Building capabilities in digital compliance tools and smart packaging technologies
- Stakeholder engagement - Active participation in industry associations and regulatory consultation processes
- Innovation partnerships - Collaborating with suppliers and technology providers to develop next-generation solutions
- Capability building - Developing internal expertise in emerging regulatory areas and compliance technologies
Conclusion
Navigating international packaging regulations requires a comprehensive understanding of diverse requirements, strategic planning, and ongoing vigilance as regulations continue to evolve. Success depends on building robust compliance systems that can adapt to changing requirements whilst maintaining operational efficiency and brand consistency.
The packaging industry is experiencing unprecedented regulatory complexity, driven by environmental concerns, consumer protection priorities, and technological advances. Companies that invest in comprehensive compliance strategies, leverage appropriate technologies, and build strong partnerships will be best positioned to succeed in this challenging environment.
At Labelprint24, we remain committed to helping our clients navigate this complex landscape with innovative solutions that meet regulatory requirements without compromising on quality, aesthetics, or functionality. Our comprehensive understanding of international regulations, combined with our technical expertise and manufacturing capabilities, enables us to deliver packaging solutions that support our clients' global ambitions whilst ensuring full compliance with applicable standards.
As regulations continue to evolve, we will continue to invest in our capabilities, expand our knowledge base, and develop new solutions that address emerging requirements. Our goal is to make international packaging compliance as straightforward as possible for our clients, allowing them to focus on growing their businesses and serving their customers.
The future of packaging regulation promises continued evolution toward greater sustainability, enhanced safety, and improved consumer protection. By staying ahead of these trends and maintaining our commitment to excellence, we help ensure that compliance becomes a competitive advantage rather than just a regulatory burden.




